Introduction
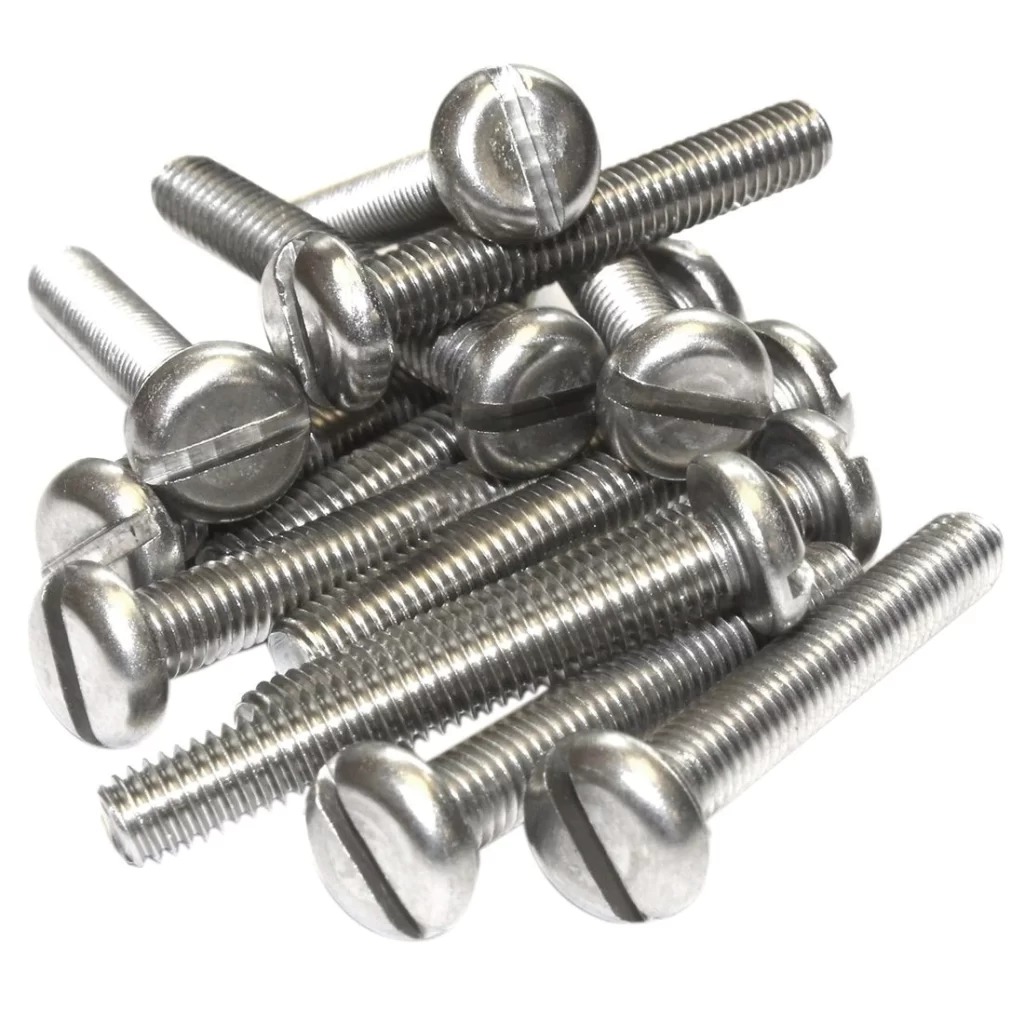
Machine screws are commonly used fasteners in various industries and applications, ranging from electronics to aerospace. These screws are designed to be threaded into tapped holes or nuts and provide a secure and reliable connection. In this guide, we will explore the different types, sizes, and applications of machine screws, as well as their materials, installation, and maintenance.
1.Definition of Machine Screws
A machine screw is a type of screw designed to be used with a threaded nut or tapped hole to form a fastening connection. Unlike wood screws or self-tapping screws, machine screws are generally used in metal-to-metal applications, and they come in a wide range of sizes and types.
2.Importance of Machine Screws
Machine screws are an essential component in many industries, as they provide a secure and reliable fastening connection that can withstand high loads and vibrations. They are commonly used in the manufacturing of electronic devices, automobiles, aircraft, and construction applications. Machine screws are also important for maintaining and repairing machinery and equipment, making them a crucial component for industrial maintenance and repair.
Types of Machine Screws
There are many different types of machine screws available, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Here are some of the most common types of machine screws:
1.Round Head Machine Screws - These screws have a round head with a flat bearing surface and a deep recessed driving slot. They are often used in applications where a low profile head is required.
2.Pan Head Machine Screws - These screws have a flat bearing surface and a rounded head that protrudes above the surface of the material it is fastening. They are commonly used in electronic and electrical applications.
3.Flat Head Machine Screws - These screws have a flat top surface and a conical bearing surface that angles down to a smaller diameter shank. They are used in countersunk holes to provide a flush surface.
4.Truss Head Machine Screws - These screws have a low, rounded, and extra wide head, which provides a large bearing surface that distributes the load over a broader area.
5.Fillister Head Machine Screws - These screws have a cylindrical head with a slightly larger diameter than the shank. They provide a smooth bearing surface and are commonly used in applications where the screw head will be visible.
6.Binding Head Machine Screws - These screws have a domed head with a flat bearing surface and a recessed driving slot. They are commonly used in applications where the screw head needs to be flush with the material surface.
7.Hex Head Machine Screws - These screws have a hexagonal head with a flat bearing surface and are tightened with a wrench or socket. They are commonly used in construction and machinery applications.
8.Socket Head Machine Screws - These screws have a cylindrical head with a recessed hexagonal socket for tightening with a wrench or hex key. They provide a high strength and a clean appearance.
9.Button Head Machine Screws - These screws have a low, rounded head with a flat bearing surface and a shallow recessed driving slot. They are used in applications where a low profile and a decorative appearance are desired.
10.Cheese Head Machine Screws - These screws have a low, cylindrical head with a flat bearing surface and a deep recessed driving slot. They are used in applications where the screw head needs to be easily accessible and tightened with a flat blade screwdriver.
Materials Used for Machine Screws
Machine screws are made from a variety of materials, depending on the specific application and requirements. Here are some of the most common materials used for machine screws:
1.Steel Machine Screws - These screws are the most common and economical type of machine screws. They are strong, durable, and are available in a wide range of sizes and configurations. They are often coated with zinc or other corrosion-resistant coatings to improve their durability.
2.Stainless Steel Machine Screws - These screws are made from a type of steel that contains chromium, which makes them highly resistant to corrosion and rust. They are commonly used in applications where high levels of hygiene or exposure to corrosive environments are a concern, such as in the food industry, marine applications, and medical equipment.
3.Brass Machine Screws - These screws are made from a type of alloy that is composed of copper and zinc, making them corrosion-resistant, decorative, and easy to machine. They are commonly used in decorative applications, such as in furniture and door hardware, as well as in electrical and electronic applications.
4.Aluminum Machine Screws - These screws are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and have good thermal and electrical conductivity. They are commonly used in applications where weight is a concern, such as in the aerospace industry, as well as in electrical and electronic equipment.
5.Nylon Machine Screws - These screws are made from a type of synthetic polymer that is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent electrical insulation properties. They are commonly used in electrical and electronic equipment, as well as in applications where weight and corrosion resistance are a concern.
6.Titanium Machine Screws - These screws are made from a lightweight and strong metal that is highly resistant to corrosion and erosion. They are commonly used in applications where high strength, low weight, and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in the aerospace and medical industries

Size and Measurement of Machine Screws
Machine screws are sized and measured based on their diameter, thread pitch, and length. Understanding these measurements is essential to selecting the appropriate screw for a specific application.
1.Diameter and Thread Pitch - The diameter of a machine screw refers to the width of the screw shaft. It is measured in fractions of an inch or millimeters. The thread pitch refers to the distance between each thread on the screw shaft and is also measured in fractions of an inch or millimeters. For example, a machine screw that is 1/4 inch in diameter with a thread pitch of 20 threads per inch is denoted as 1/4-20.
2.Length - The length of a machine screw is measured from the bottom of the head to the tip of the screw. It is also measured in fractions of an inch or millimeters. Machine screws are available in a wide range of lengths, from very short screws to those that are several inches long.
It is important to choose the appropriate size and length of machine screw for the intended application to ensure the screw provides the necessary strength and stability.
Applications of Machine Screws
Machine screws are used in a wide range of industries and applications, thanks to their versatility and strength. Here are some of the most common applications of machine screws:
1.Aerospace Industry - Machine screws are used extensively in the aerospace industry, where they are used to fasten various components and structures together. The screws used in this industry must be lightweight, strong, and able to withstand high levels of stress and pressure.
2.Automotive Industry - Machine screws are used in the automotive industry to fasten various components of vehicles together. They are used in engines, transmissions, and other critical components where strength and reliability are essential.
3.Electronics Industry - Machine screws are used in the electronics industry to fasten electronic components to circuit boards and other structures. They are available in a variety of materials, including nylon and stainless steel, which makes them ideal for use in electrical and electronic equipment.
4.Construction Industry - Machine screws are used in the construction industry to fasten various components of buildings and structures together. They are commonly used in metal framing, drywall, and other applications where a strong and secure fastening is required.
5.Medical Industry - Machine screws are used in the medical industry to fasten various components of medical devices together. They are used in surgical instruments, implants, and other medical equipment where strength and biocompatibility are essential.
In conclusion, machine screws are used in a wide range of industries and applications, thanks to their strength, versatility, and durability.
Installation of Machine Screws
Proper installation of machine screws is critical to ensure their effectiveness and reliability. Here are some considerations and steps to follow when installing machine screws:
1.Pre-Installation Considerations - Before installing machine screws, it is important to consider the materials being fastened together, the size and length of the screw, and the torque requirements of the application. The screw must be long enough to provide sufficient engagement and strength but not too long that it damages the material.
2.Tools Required - The tools required to install machine screws include a screwdriver, wrench, or drill depending on the type of screw and application. A torque wrench may also be required to ensure the proper amount of torque is applied to the screw.
3.Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Machine Screws - Here are the general steps to follow when installing machine screws:
- Determine the correct size and length of the screw for the application.
- Place the screw in the hole, making sure it is aligned with the thread and the hole is deep enough for the screw to be fully engaged.
- Use the screwdriver, wrench, or drill to turn the screw clockwise, applying enough force to ensure the screw is secure but not so much that it damages the material.
- If using a torque wrench, apply the appropriate amount of torque to the screw according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- If necessary, use a washer or lock washer to ensure a secure and tight fit.
Proper installation of machine screws is critical to ensure the effectiveness and reliability of the fastening. By following these steps and using the appropriate tools and techniques, machine screws can provide a secure and lasting hold in a variety of applications.
Maintenance and Care of Machine Screws
Proper maintenance and care of machine screws can extend their lifespan and ensure they continue to function effectively. Here are some key maintenance and care practices for machine screws:
1.Inspection - Regular inspection of machine screws is essential to identify any signs of wear or damage. Look for signs of corrosion, bending, or other damage that may affect the screw’s effectiveness. If damage is identified, the screw should be replaced.
2.Cleaning and Lubrication - Regular cleaning and lubrication can help to prevent corrosion and ensure the screw operates smoothly. Use a soft brush or cloth to remove any dirt or debris from the screw and apply a suitable lubricant, such as silicone or lithium grease.
3.Replacement - Machine screws should be replaced if they are worn, damaged, or no longer effective. When replacing a screw, ensure the new screw is the appropriate size and length for the application.
It is also important to store machine screws properly to prevent damage and corrosion. Store screws in a dry, cool place away from direct sunlight and moisture.By following these maintenance and care practices, machine screws can provide a reliable and effective fastening solution for a range of applications.

Conclusion
Machine screws are an essential fastening solution in many industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, construction, and medical. In this article, we have covered the different types, materials, sizes, and applications of machine screws, as well as the importance of proper installation, maintenance, and care.
Here is a summary of the key points covered:
- Machine screws come in different types, including round head, pan head, flat head, and hex head, among others.
- Materials used for machine screws include steel, stainless steel, brass, aluminum, nylon, and titanium, among others.
- Machine screws are available in different sizes and measurements, including diameter, thread pitch, and length.
- Machine screws are used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, construction, and medical.
- Proper installation, maintenance, and care of machine screws are essential to ensure their effectiveness and reliability.
- Future advancements in technology may lead to the development of more advanced machine screws with improved strength, durability, and functionality.
In conclusion, machine screws are a crucial component in many industries, providing reliable and secure fastening solutions. By following proper installation and maintenance practices, machine screws can continue to serve their purpose effectively and efficiently.