I. Introduction
A. What are CNC machined parts?
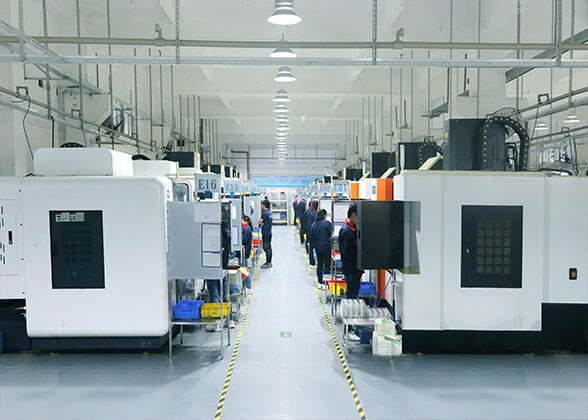
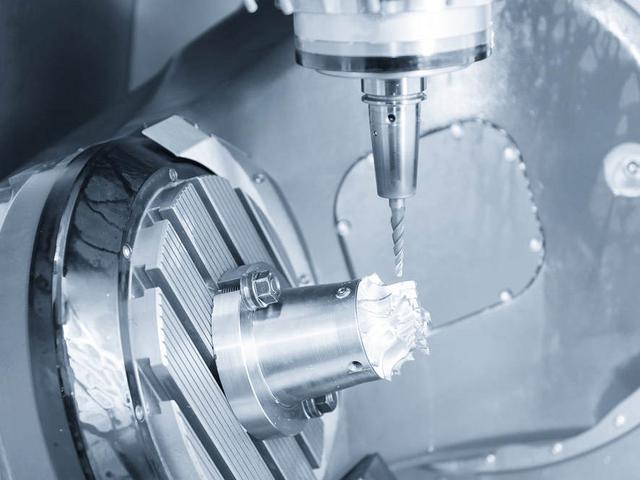
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled machines to remove material from a workpiece to create a final part or product. CNC machined parts are components that have been produced through this process, where precise cuts and shapes are made using CNC machines.
B. Why are CNC machined parts important?
CNC machined parts are essential in modern manufacturing because they offer a level of accuracy, consistency, and complexity that is difficult to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods. CNC machines can create intricate designs and shapes with ease, and the process can be automated, reducing the risk of errors and increasing productivity. CNC machined parts are used in a wide range of industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical and electronics, and are critical components in the production of high-quality products.
II. CNC Machining Process
A. Understanding the CNC machining process
The CNC machining process involves a computer-controlled machine that uses pre-programmed instructions to move cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. The process begins with a 3D design file, which is imported into a CNC machine’s software. The software then generates toolpaths and sends the instructions to the machine to produce the desired part.
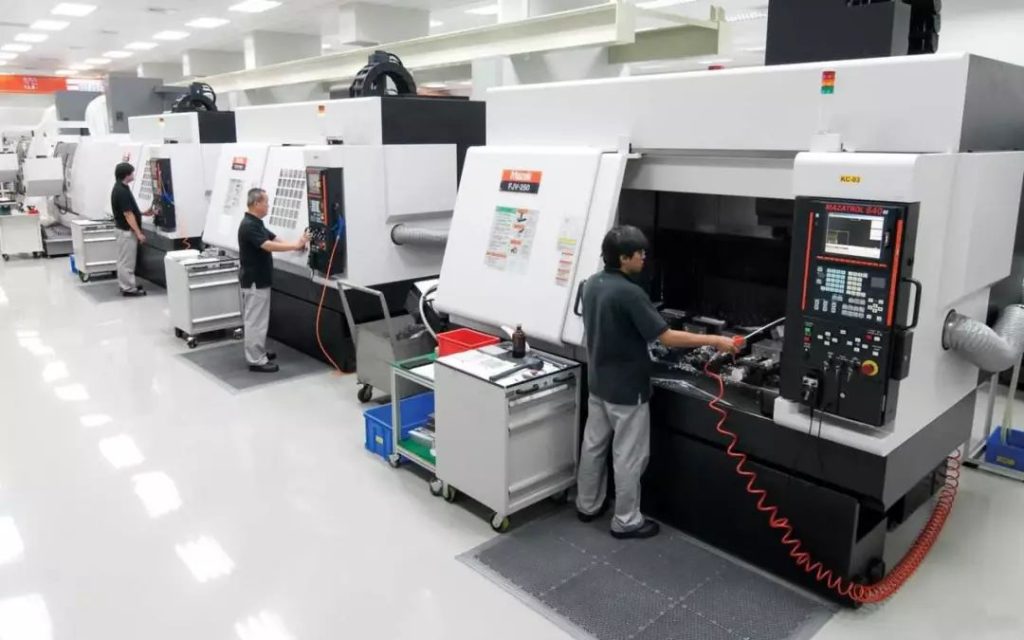
B. Types of CNC machines
There are several types of CNC machines, each designed to handle specific tasks. Some common types of CNC machines include:
1.CNC milling machines:used to remove material from a workpiece by rotating cutting tools
2.CNC lathes:used to produce cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece while cutting tools move along it
3.CNC routers: used to cut and shape materials like wood, plastic, and composites
4.CNC plasma cutter:used to cut metal using a plasma torch
C. Materials used in CNC machining
CNC machines can work with a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, composites, and even wood. Some common materials used in CNC machining include:
1.Aluminum:lightweight and durable, often used in aerospace and automotive industries
2.Stainless steel: strong and corrosion-resistant, often used in medical and food industries
3.Plastics:versatile and lightweight, often used in electronics and consumer goods industries
4.Titanium:strong and lightweight, often used in aerospace and medical industries
5.Composites:lightweight and strong, often used in aerospace and automotive industries.
III. Designing for CNC Machining
A. Design considerations for CNC machining
Designing for CNC machining requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
1.Material selection:the material chosen for the part will affect the machining process and the final product’s quality and durability.
2.Part orientation:the orientation of the part in the machine will affect the cutting process and the accuracy of the final product.
3.Tool selection: the type of cutting tool used will depend on the material and the desired finish.
4.Tolerance and surface finish:CNC machines can achieve high levels of precision, so designing for tight tolerances and specific surface finishes can help achieve the desired result.
B. CAD software for CNC machining
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is essential for designing parts for CNC machining. CAD software allows engineers to create detailed 3D models of parts, which can be used to generate toolpaths for CNC machines. Some popular CAD software programs used in CNC machining include SolidWorks, Autodesk Inventor, and Fusion 360.
C. CAM software for CNC machining
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software is used to generate toolpaths from 3D models created in CAD software. CAM software takes into account the cutting tools, material, and machine parameters to generate instructions for the CNC machine. Some popular CAM software programs used in CNC machining include Mastercam, GibbsCAM, and BobCAD.
IV. CNC Machining Techniques
A. Cutting techniques for CNC machining
Cutting is the most common technique used in CNC machining. The cutting technique involves removing material from a workpiece using a cutting tool. Some common cutting techniques used in CNC machining include:
1.Milling:involves rotating a cutting tool and moving it across the surface of the workpiece to remove material
2.Turning:involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool moves along it to remove material and create cylindrical shapes
3.Routing:involves cutting material using a spinning cutting tool that moves along a predetermined path
B. Drilling techniques for CNC machining
Drilling is another common technique used in CNC machining. The drilling technique involves creating holes in the workpiece using a drill bit. Some common drilling techniques used in CNC machining include:
1.Peck drilling:involves drilling a hole in increments to avoid overheating the drill bit and breaking it
2.Counterboring:involves drilling a larger hole to allow for the insertion of bolts or screws
3.Spot drilling:involves drilling a small hole to mark the location of a larger hole to be drilled later
C. Turning techniques for CNC machining
Turning is a technique used to create cylindrical parts, such as shafts or sleeves. Turning involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool moves along it to remove material and create the desired shape. Some common turning techniques used in CNC machining include:
1.Facing:involves cutting the surface of the workpiece to create a flat surface
2.Taper turning:involves cutting the surface of the workpiece at an angle to create a taper
3.Thread turning:involves cutting threads onto the surface of the workpiece to create screw threads.
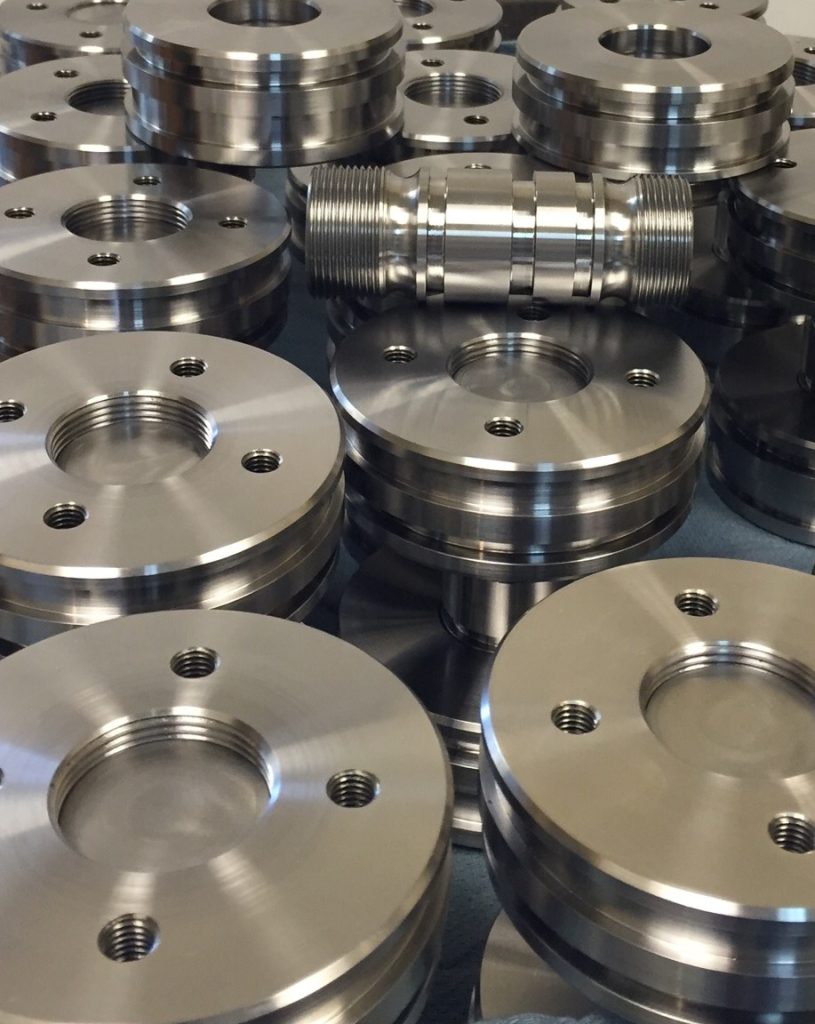

V. Finishing Techniques
A. Surface finishing techniques for CNC machined parts
Surface finishing is a process used to enhance the appearance and functionality of CNC machined parts. Some common surface finishing techniques used in CNC machining include:
1.Sandblasting:involves using high-pressure air or water to blast abrasive particles onto the surface of the part to create a uniform texture.
2.Anodizing:involves using an electrochemical process to coat the surface of the part with a protective and decorative oxide layer.
3.Painting:involves applying a layer of paint or coating onto the surface of the part to provide protection or enhance its appearance.
B. Deburring techniques for CNC machined parts
Deburring is a process used to remove rough edges or burrs from CNC machined parts. Burrs are small metal shavings that are left behind after the cutting process. Some common deburring techniques used in CNC machining include:
1.Manual deburring:involves using handheld tools such as files, scrapers, and sandpaper to remove burrs and sharp edges.
2.Vibratory finishing:involves placing the parts in a container with abrasive media and vibrating the container to remove burrs and smooth the surface.
3.Thermal deburring:involves using a combination of heat and oxygen to remove burrs from the part’s surface.
C. Polishing techniques for CNC machined parts
Polishing is a process used to create a smooth and shiny surface on CNC machined parts. Some common polishing techniques used in CNC machining include:
1.Buffing:involves using a polishing wheel or buffing pad to apply a polishing compound to the surface of the part to create a shiny surface.
2.Electropolishing:involves using an electrochemical process to remove a thin layer of the surface of the part to create a smooth and shiny surface.
3.Tumbling:involves placing the parts in a container with abrasive media and rotating the container to create a smooth and polished surface.
VI. Quality Control
A. Inspection techniques for CNC machined parts
Inspection is an important part of the CNC machining process to ensure the parts meet the required specifications. Some common inspection techniques used in CNC machining include:
1.Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs):involves using a machine to measure the dimensions and features of the part to ensure they meet the required specifications.
2.Optical inspection:involves using a microscope or other optical equipment to inspect the part’s surface for defects, such as cracks or scratches.
3.Surface roughness measurement:involves using equipment to measure the surface roughness of the part to ensure it meets the required specifications.
B. Quality control measures for CNC machining
Quality control measures are important to ensure the CNC machining process produces parts that meet the required specifications. Some common quality control measures used in CNC machining include:
1.Documented procedures:involves creating documented procedures for each step of the CNC machining process to ensure consistency and accuracy.
2.Calibration:involves regularly calibrating the CNC machine and inspection equipment to ensure accurate and consistent measurements.
3.Statistical process control (SPC):involves using statistical methods to monitor the CNC machining process and detect any deviations from the expected results.
VII. Applications of CNC Machined Parts
A. Industries that use CNC machined parts
CNC machined parts are used in a wide variety of industries, including:
1.Aerospace:CNC machined parts are used in aircraft components such as engine parts, landing gear, and structural components.
2.Automotive:CNC machined parts are used in various automotive components such as engine blocks, transmission parts, and brake components.
3.Medical:CNC machined parts are used in medical devices and implants such as joint replacements, surgical tools, and dental implants.
4.Electronics:CNC machined parts are used in electronic components such as circuit boards, heat sinks, and enclosures.
B. Examples of CNC machined parts in everyday life
CNC machined parts are used in many everyday objects, such as:
1.Smartphones:CNC machined parts are used in smartphone components such as the casing, camera modules, and buttons.
2.Watches:CNC machined parts are used in the production of watch components such as the case, crown, and movement.
3.Kitchen appliances:CNC machined parts are used in the production of kitchen appliances such as blenders, coffee makers, and toasters.
4.Sporting goods:CNC machined parts are used in the production of sporting goods such as golf clubs, bicycle components, and fishing reels.
VIII. Advantages and Limitations of CNC Machining
A. Advantages of CNC machining
CNC machining offers several advantages over traditional machining methods, including:
1.Precision - CNC machining offers precise and accurate cuts, ensuring high-quality and consistent parts.
2.Efficiency - CNC machining can produce parts quickly and efficiently, reducing production time and costs.
3.Flexibility - CNC machines can be programmed to produce a wide range of parts, making them versatile and adaptable to different applications.
4.Automation - CNC machines can be automated, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing production efficiency.
B. Limitations of CNC machining
While CNC machining offers several advantages, it also has some limitations, including:
1.Cost - CNC machines can be expensive to purchase and maintain, making them less accessible for small-scale production.
2.Complexity - Programming CNC machines can be complex, requiring skilled operators and specialized software.
3.Material limitations - CNC machining is limited to certain materials, such as metals and plastics, and may not be suitable for more brittle materials such as ceramics or glass.
4.Size limitations - CNC machines have size limitations, making it difficult to produce very large or very small parts.
IX. Future of CNC Machining
A. Trends in CNC machining
CNC machining is a rapidly evolving field, and some current trends include:
1.Additive manufacturing - the integration of additive manufacturing techniques with CNC machining, allowing for more complex designs and faster prototyping.
2.Automation - increased automation of CNC machines, reducing the need for human intervention and increasing efficiency.
3.Industry 4.0 - the integration of CNC machines with the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics, allowing for real-time monitoring and optimization of the machining process.
4.Sustainable manufacturing - the integration of sustainable practices in the CNC machining process, such as the use of environmentally friendly materials and energy-efficient processes.
B. Emerging technologies in CNC machining
Some emerging technologies in CNC machining include:
1.Nanotechnology - the use of nanotechnology in CNC machining, allowing for the production of extremely small and precise parts.
2.Artificial intelligence - the use of artificial intelligence in CNC machining, allowing for more efficient and accurate programming and operation of CNC machines.
3.3D printing - the integration of 3D printing with CNC machining, allowing for the production of complex geometries and reducing the need for assembly.
4.Quantum computing - the use of quantum computing in CNC machining, allowing for faster and more accurate simulations and optimization of the machining process.

X. Conclusion
CNC machining is a versatile and efficient method for producing high-quality and precise parts. In this article, we have explored the CNC machining process, design considerations, cutting techniques, finishing techniques, quality control measures, and applications of CNC machined parts. We have also discussed the advantages and limitations of CNC machining and some emerging technologies and trends in the field.
CNC machining is a rapidly evolving field that is transforming the way we produce parts and objects. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovation and integration of emerging technologies with CNC machining. Despite its limitations, CNC machining offers a precise, efficient, and flexible method for producing high-quality parts, making it a valuable tool for various industries and applications.