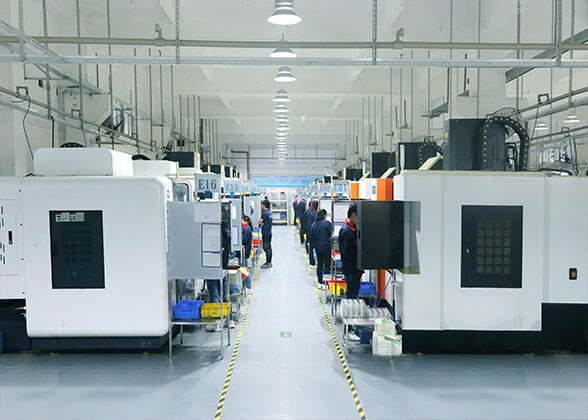
When machine tools are used to process steel parts, some processing methods are often used. For example, change the properties of steel and make it easier to process, and treat the steel after processing to improve the strength or hardness of the finished product. Three common steel processing technologies are as follows.
Heat treatment
Heat treatment refers to several different processes that involve manipulating the temperature of steel to cnc machined metal parts.
Annealing, reducing hardness, increasing ductility, making steel easier to process. During annealing, the steel is slowly heated to the required temperature for a period of time. The time and temperature required depend on the specific alloy and decrease with the increase of carbon content. Finally, the steel is cooled slowly in the furnace.
Normalizing can reduce the internal stress of steel while maintaining higher strength and hardness than annealing steel. During the normalizing process, the steel is heated to a high temperature and then cooled at a suitable temperature to improve the hardness of the steel.
Quenching will harden the steel and increase its strength, but will make it more brittle. During quenching, the steel shall be heated slowly. After a period of time, the steel shall be immersed in liquid such as water, oil or salt solution for rapid cooling.

Tempering reduces the hardness of steel and increases toughness. Tempering is similar to normalizing. First, the steel is heated to the set temperature, maintained for a period of time, and then naturally cooled. The difference is that the tempering temperature is lower.
Precipitation hardening
Precipitation hardening improves the yield strength of steel. In order to activate precipitation hardenability, the steel is first solution treated and then age hardened. The aging hardening process increases the strength of the material - the material is heated for a long time to produce sediment, forming solid particles of various sizes.

17 – 4 PH (also known as 630 steel) is a common example of a precipitation hardening grade of stainless steel. This alloy contains 17% chromium, 4% nickel and 4% copper. Due to its increased hardness, strength and high corrosion resistance, 17 – 4 pH is used for helicopter platforms, turbine blades and nuclear waste drums.
Cold working
Modification can also change the properties of steel without increasing too much heat. For example, cold worked steel becomes stronger through the work hardening process. Work hardening occurs when a metal undergoes plastic deformation. This allows you to deliberately hammer, roll, or pull the metal. When cutting tools or workpieces are at high temperatures, hardening of workpieces may also occur intentionally during machining. Cold working also improves the machinability of steel. Cold working also improves the machinability of steel.

Problems in steel structure design
When designing steel parts, it is important to keep in mind the unique properties of materials. Features that are appropriate for your application may require some additional Design for Manufacturing (DFM) considerations.
Because of the hardness of the material, machined steel will have a longer service life than other softer materials (such as aluminum or brass), and you can protect your parts and tools by reducing the spindle speed and feed rate.
Machinability and differences in hardness and strength must be considered when deciding which steel to use. For example, the processing time of stainless steel is about twice that of carbon steel. When determining different grades, it is necessary to consider which properties are most important and which steel alloys are easy to obtain. Common grades (such as 304 or 316 stainless steel) have a wider range of stock sizes to choose from, and require less time to find and purchase.